You're navigating the complex landscape of nutrition, and understanding the glycemic index is like having a compass to guide your choices. Imagine being equipped with the knowledge to make informed decisions about the foods you consume, and how they affect your body's blood sugar levels. As you dive into this discussion, you'll uncover the subtle yet profound ways in which the glycemic index influences your overall well-being, and discover practical strategies for incorporating low glycemic index foods into your daily routine. This knowledge could be the missing piece in your quest for a balanced and healthier lifestyle, so let's explore together how Lean Bliss can shed light on this crucial aspect of nutrition.
What Is the Glycemic Index?
Understanding the glycemic index involves evaluating how different foods affect blood sugar levels after consumption. The glycemic index measures the rise in blood sugar after consuming carbohydrates and is expressed on a scale of 0 to 100. Foods with a high glycemic index cause a rapid increase in blood sugar, while those with a low index cause a slower, more gradual rise. This is important for overall health, as high levels of blood sugar can lead to weight gain, diabetes, and other health issues.
The glycemic index was invented in 1981 by physicians David Jenkins and Thomas Wolever. It is the percentage by which a food raises blood sugar compared to glucose. Balanced meals typically contain foods with different glycemic indices, making the glycemic index of an individual food in a meal insignificant. Recent studies have shown mixed results regarding the effectiveness of glycemic index. The American Diabetes Association emphasizes that the amount of carbohydrate in a food is more important than its glycemic index for individuals with diabetes.
A low-glycemic index diet may improve insulin sensitivity in children with obesity and elevated insulin and can be used to prevent diabetes, heart disease, and obesity according to the International Carbohydrate Quality Consortium. Therefore, understanding the glycemic index can be beneficial for blood sugar regulation, weight loss, and overall health.
Impact on Blood Sugar Levels
The impact of different foods on blood sugar levels can vary significantly based on their glycemic index. Understanding the glycemic index is crucial for maintaining healthy blood glucose levels, especially for individuals on a weight management journey. Foods with a low glycemic index are beneficial for stabilizing blood sugar levels and promoting weight loss. They have a smaller impact on blood sugar levels, which can prevent energy crashes and reduce fat storage. By incorporating low glycemic index foods into your diet, you can enhance energy utilization and overall health.
Incorporating ingredients like Ceylon Cinnamon Bark into your meals can aid in regulating blood sugar and contribute to stabilizing blood glucose levels. This is particularly important for individuals focused on healthy weight management, as it supports the body in efficiently processing energy and nutrients. By paying attention to the glycemic index of the foods you consume, you can make informed choices that positively impact your blood sugar levels and overall well-being. Whether your goal is weight loss or simply maintaining a healthy lifestyle, being mindful of the glycemic index can play a significant role in achieving your desired outcomes.
Using GI for Food Choices

Now that you understand the basics of the Glycemic Index (GI), it's time to put that knowledge into practice. By using GI for food choices, you can make healthier decisions that support your overall well-being. Opting for low GI foods over high GI options can help you maintain balanced blood sugar levels and avoid energy crashes.
GI for Health
To make informed choices for your health, consider the glycemic index (GI) of foods to manage blood sugar levels and support weight management goals. The GI of food indicates how it affects blood sugar levels after consumption. Choosing foods with a lower GI can contribute to a more balanced approach to blood sugar regulation. This is important for overall effectiveness in managing blood sugar levels, especially for individuals with diabetes or those aiming to prevent spikes and crashes associated with high-carbohydrate meals. Incorporating low GI foods into your diet can support weight management and a healthy diet. It can help in curbing appetite, reducing calorie intake, and ultimately supporting weight loss goals. Additionally, being mindful of the GI can guide you towards making healthier food choices, such as opting for foods with lower GI and those that contain sugar alcohol.
Low Vs High
Considering the impact of low and high glycemic index (GI) foods is crucial when making informed choices for your health and managing blood sugar levels and weight. When it comes to using GI for food choices, opting for low GI foods can aid in regulating blood sugar and promoting healthy weight loss. On the other hand, high GI foods can lead to rapid spikes in blood sugar levels and may hinder weight management efforts. Understanding the glycemic index can help you make informed decisions to support a healthy diet and overall effectiveness in managing your well-being. Here are some key points to remember:
- Low GI foods release glucose slowly, providing sustained energy and promoting satiety.
- High GI foods cause rapid spikes and crashes in blood sugar, leading to increased hunger and potential fat storage.
- Choosing low GI options can aid in regulating blood sugar and promoting healthy weight loss.
- High GI foods may contribute to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes, while low GI foods can support blood sugar regulation and weight management.
Balanced Meal
When planning a balanced meal, understanding the glycemic index (GI) of foods can help you make informed choices to stabilize blood sugar levels and promote overall health. A balanced approach to meal planning involves incorporating foods with low to moderate GI values, such as whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and plenty of fruits and vegetables. This approach plays a crucial role in weight management and healthy weight loss by preventing spikes and crashes in blood glucose levels associated with high-carbohydrate meals. By regulating blood sugar, the GI can control appetite, support energy levels, and enhance overall well-being. When considering the glycemic index of foods alongside other nutritional qualities, you can make practical and effective meal choices to support your health goals.
| Low GI | Moderate GI | High GI |
|---|---|---|
| Apples | Brown rice | White bread |
| Lentils | Oatmeal | Watermelon |
| Yogurt | Sweet potato | Cornflakes |
| Nuts | Quinoa | Pineapple |
| Broccoli | Carrots | Baguette |
Low Vs. High GI Foods
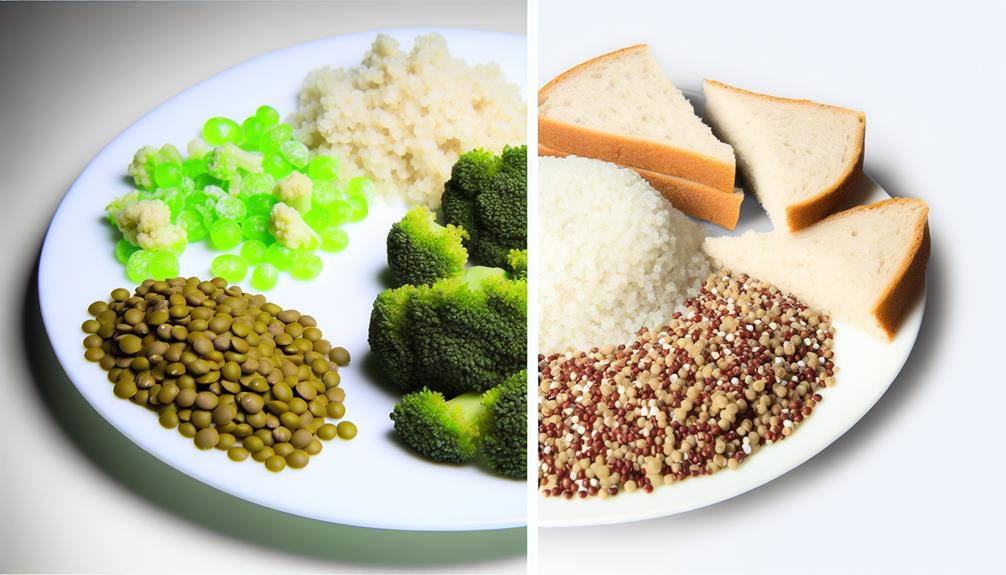

Opt for low glycemic index (GI) foods to support stable blood sugar levels and sustained energy. Low GI foods are digested and absorbed slowly, leading to a gradual rise in blood sugar levels. This slow digestion can help in managing weight by promoting fullness and providing sustained energy throughout the day. On the other hand, high GI foods are quickly digested and absorbed, causing a rapid spike in blood sugar levels. This rapid increase in blood sugar may lead to increased hunger and overeating due to subsequent blood sugar crashes.
Incorporating low GI foods into your diet can be beneficial for weight management as they can help in preventing fat storage and supporting overall effectiveness in maintaining a healthy weight. Consuming a balanced approach with a mix of low and high GI foods can help in maintaining stable blood sugar levels and supporting a healthy diet. By including low GI foods in your meals, you can better manage your food intake and support weight loss efforts effectively. Therefore, opting for a diet that includes a variety of low GI foods can contribute to a healthy lifestyle and aid in weight management.
Benefits of Choosing Low GI Foods
When choosing low GI foods, you can benefit from healthier blood sugar levels, which can lead to sustained energy throughout the day. This can help you avoid the energy crashes often associated with high-GI foods, allowing you to maintain a more consistent level of vitality. By making this choice, you're setting yourself up for better overall health and improved energy levels.
Healthier Blood Sugar Levels
By choosing low glycemic index (GI) foods, you can effectively support healthier blood sugar levels and avoid the spikes and crashes associated with high-carbohydrate meals. This choice can aid in maintaining stable blood sugar levels and contribute to a healthy diet. Additionally, low GI foods can help with weight loss efforts by reducing fat storage and increasing energy utilization. They also aid in curbing excessive insulin release, further supporting weight loss goals. When opting for low GI foods, you are embracing a holistic approach to managing blood sugar levels and overall health. Consider incorporating natural compounds like Kudzu Flower Extract, Corosolic acid, and Citrus Sinensis into your diet to further support healthy blood sugar levels.
Sustained Energy Throughout Day
To maintain sustained energy throughout the day, choosing low GI foods can be beneficial for stabilizing blood sugar levels and supporting weight management. Low GI foods have a gradual effect on blood sugar levels, providing a steady release of energy. This can help regulate blood sugar levels, preventing energy crashes and supporting healthy weight loss. By incorporating low GI foods into your diet, you can promote a healthy metabolism and blood sugar balance, which is essential for sustained energy throughout the day. Additionally, combining a low GI diet with regular exercise can further enhance the benefits of sustained energy and healthy weight management.
| Benefits of Low GI Foods |
|---|
| Regulates Blood Sugar Levels |
| Supports Healthy Weight Loss |
| Promotes Sustained Energy |
Balancing Meals With GI
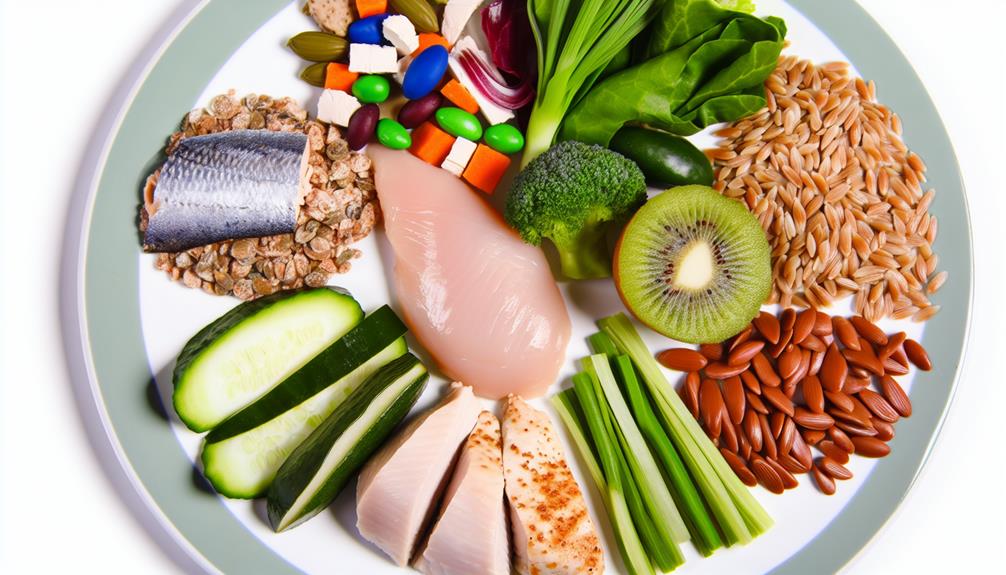

Balancing your meals with the Glycemic Index (GI) involves strategically combining high and low GI foods to maintain consistent blood sugar levels throughout the day. By balancing meals with GI, you can support weight management, stabilize blood sugar, and promote overall metabolic health. To achieve this, consider the following:
- Pair high GI foods with low GI foods: Combining high GI foods like white bread or rice with low GI foods such as lean proteins, healthy fats, and non-starchy vegetables can help regulate the impact on blood sugar levels.
- Include protein, healthy fats, and fiber: Incorporating these nutrients with high GI foods can slow down the absorption of glucose, preventing sudden spikes in blood sugar and promoting sustained energy levels.
- Choose whole grains and legumes: Opt for whole grains, legumes, and non-starchy vegetables alongside high GI foods to create a more balanced and sustained release of energy, supporting healthy weight loss and reducing cravings.
- Understand the impact of different foods: By being mindful of the glycemic index of foods and combining them strategically, you can support a healthy diet and stabilize blood sugar levels throughout the day.
Balancing meals with GI is not only a weight loss aid but also a crucial component of maintaining healthy blood sugar levels and overall well-being. Incorporating these strategies into your meal planning can contribute to a more balanced and sustained energy throughout the day.
Practical Tips for Applying GI
When incorporating the glycemic index into your meal planning, it is essential to consider practical tips for applying GI to create balanced and nutritious meals. Understanding the glycemic index can be a valuable tool in achieving healthy weight loss and supporting overall healthy blood sugar levels. Here are some practical tips for applying GI to your diet.
First, choose whole grains such as whole grain bread, pasta, and rice. These options have a lower glycemic index compared to their refined counterparts, making them a better choice for managing blood sugar levels and weight.
Pairing foods wisely is another beneficial strategy. By combining high GI foods with low GI foods, you can create balanced, moderate GI meals that provide sustained energy and promote a healthy weight.
Additionally, adding lean proteins and healthy fats to your meals can help lower the overall glycemic impact. Foods like avocado or nuts not only contribute to a feeling of fullness but also aid in stabilizing blood sugar levels.
Watching portion sizes is crucial for managing the overall glycemic load of a meal. Even if individual foods have a high GI, controlling portion sizes can help mitigate their impact.
Finally, consider cooking methods. Opt for steaming or boiling over frying, as these methods can help lower the glycemic index of certain foods.
Incorporating these practical tips for applying GI into your meal planning can contribute to a balanced approach to weight management and support a healthy diet.
Incorporating Lean Bliss Principles
Incorporating Lean Bliss principles can further enhance your efforts to stabilize blood sugar levels and support a balanced approach to weight management and a healthy diet. By integrating Lean Bliss into your routine, you can aid in maintaining healthy blood sugar levels and supporting effective weight loss. Here are some practical ways to incorporate Lean Bliss principles into your lifestyle:
- Utilize the glycemic index: Understanding the glycemic index of foods can help you make informed choices to support healthy blood sugar levels and weight management.
- Support healthy weight: Lean Bliss contains natural compounds that may aid in weight management, helping you achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
- Aid in effective weight loss: By stabilizing blood sugar levels, Lean Bliss can support your weight loss efforts by helping to control appetite and manage calorie intake.
- Promote a healthy diet: Incorporating Lean Bliss can help you maintain a balanced and healthy diet by supporting stable blood sugar levels and energy utilization.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do You Understand the Glycemic Index?
When you understand the glycemic index, you grasp the impact of sugar on blood sugar levels after eating carbs. This knowledge guides your carb choices, helping manage blood sugar and energy levels. It also aids in weight management, nutrient absorption, and digestive health. By planning meals with a focus on glycemic load, you can promote sustained satiety and stable energy throughout the day.
What Are the Top 10 Low Glycemic Foods?
To maintain stable blood sugar and support weight management, include lentils, nuts, cherries, grapefruit, yogurt, milk, apples, pears, barley, and beans in your meal planning. These low glycemic foods aid in digestive health, provide sustained energy, and support healthy snacking. Their nutrient content and cooking methods can help control blood sugar and promote steady energy levels. Incorporating these foods into your diet supports overall health, making wise food choices and exercise benefits more manageable.
How Do You Check the Glycemic Index of Foods?
To check the glycemic index of foods, you can use GI testing methods and consider carbohydrate quality and glycemic load calculation. Pay attention to fiber content, portion control, and food processing which can impact blood sugar levels. Meal combinations also affect the glycemic response and energy levels. It's important to look for official glycemic index measurements from reliable sources and consult a nutrition professional for a better understanding of the glycemic index in your diet.
What Are High GI Foods to Avoid?
When it comes to high GI foods to avoid, it's important to steer clear of processed carbs like white bread, refined grains, and instant rice. Additionally, keep an eye out for sugary treats such as snack bars, breakfast cereals, and sweetened beverages. Starchy vegetables and high GI fruits like watermelon and ripe bananas should also be consumed in moderation. By being mindful of these foods, you can better manage your glycemic index intake.
